|
Converter-Concepts / Cooling |

|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
CERN
|
SY-EPC
|
EDMS
|
PROJECTS
|
ODF
/
OOXML
|
|
CERN
|
SY-EPC
|
EDMS
|
PROJECTS
|
ODF
/
OOXML
|
|
|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material | Demineralised Environment | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Erosion | Corrosion | Comments | |
| Inox-316 | N.A. |
N.A. |
Use whenever possible. L or Ti version (extra-low carbon) recommended if soldered. Considered as non-magnetic. Great care regarding Chlore pollution (close cleanning + solder action). |
| Copper | Critical at Vfluid > 3 m/s. (geometry and T°C dependant). | Corrosion expected. (O2 concentration). | Soft material, to be used when thermal conductivity is key factor. Discontinuities (joint, solders...) are highly critical, especially at high T°C (> 60°C). Curves shall respect minimum curvature of xx x diameter. |
Recommended Material Table for water layout elements.
- Some material are particulary not compatible with CERN environment (demineralised water, several stop/restart of flow fluid, fluid velocity...). These inadequate materials can lead to critical failure after some years of operation only. ...
Material Galvanic Compatibility
It is recommended to consider the potential difference (DDP) between metals in contact to prevent galvanic effect.
Galvanic compatibility is especially a concern when using Aluminium material, in environment with high humidity. See some examples:
Copper - Aluminium:
Couple not suitable for humid environment (corrosive effect on aluminium), since total |DDP| > 0.45V.
Copper* - Aluminium:
* with Sn surface treatment on copper to improve material compatibility.
Couple suitable for humid environment (low corrosive effect on aluminium, since DDP < 0.25V)..
Copper - Aluminium:
Couple not suitable for humid environment (corrosive effect on aluminium), since total |DDP| > 0.45V.
| Heat-sink and bottom Plate: | Aluminium | DDP=-0.75V |
|---|---|---|
| Water Pipe: | Copper (no treat.) | DDP=-0.30V |
| Assembly: | Cu-Al | |DDP|(Cu–Al)=0.45V |
Copper* - Aluminium:
* with Sn surface treatment on copper to improve material compatibility.
Couple suitable for humid environment (low corrosive effect on aluminium, since DDP < 0.25V)..
| Heat-sink and bottom Plate: | Aluminium | DDP=-0.75V |
|---|---|---|
| Water Pipe: | Copper + Sn treat. | DDP=-0.50V |
| Assembly: | Sn-Al | |DDP|(Sn–Al)=0.25V |
- Reference: Compatilibité Galvanique (source: Jacques Dubois) .pdf
Material Degradation
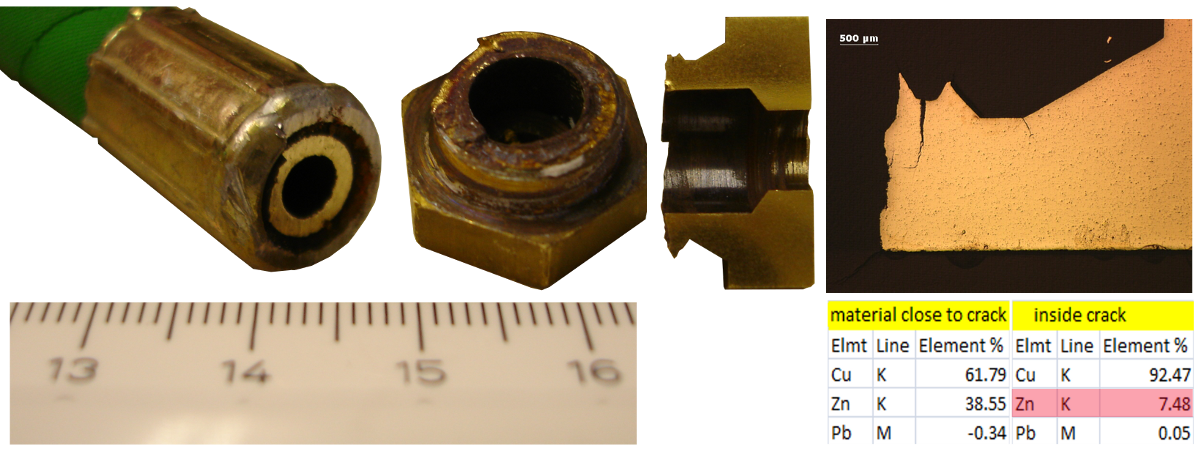
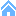
Erosion in copper can be highly critical. It mailny depends on:
- Discontinuities in the layout. (solder)
- Too sharp curves piping
- Temperature of the water.
- 0.1mm material loss after 30 years at 6 m/s at T°C < 50°C on straight section, without any discontinuity.
- 1.0mm material loss after 25 years at 9m/s T°C = 40°C on sections presenting some discontinuity.
 Validation
Validation
 Example
Example
| TOP | CHARTE | HTML | CSS | Ver : 18-12-2020 20:53:45 | Webmaster : Michel GEORGES. |